Services
We Provide
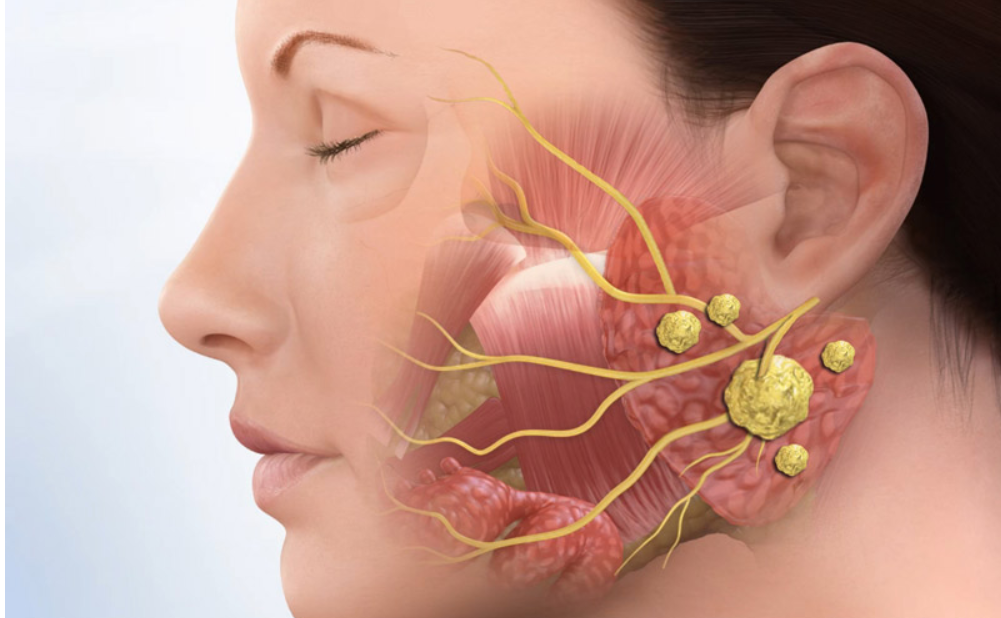
Understanding Salivary Gland Duct Stones
Salivary gland duct stones, also known as sialolithiasis, are calcified deposits that form within the ducts of the salivary glands, obstructing the flow of saliva. These stones can cause discomfort, swelling, and other symptoms, affecting the function of the affected salivary gland. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for salivary gland duct stones is essential for effectively managing this condition and preventing complications.
Diagnosis of Salivary Gland Duct Stones
Diagnosing salivary gland duct stones typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider, often an otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat specialist) or a dentist. During the examination, the provider may review the individual’s medical history and perform tests such as:
- Physical Examination: A physical examination of the mouth, neck, and salivary glands to assess for signs of swelling, tenderness, or palpable stones.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging studies such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scans, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be recommended to visualize the salivary glands and detect the presence of stones.
- Salivary Gland Function Tests: Salivary gland function tests, such as sialography or salivary flow rate measurement, may be performed to assess saliva production and ductal patency.
Causes of Salivary Gland Duct Stones
Salivary gland duct stones form when minerals such as calcium or phosphate accumulate and harden within the ducts of the salivary glands. Several factors may contribute to the development of salivary gland duct stones, including:
- Dehydration: Decreased saliva production due to dehydration can lead to the concentration of minerals in the saliva, increasing the risk of stone formation.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate oral hygiene practices such as infrequent brushing or flossing can contribute to the buildup of bacteria and debris in the salivary ducts, leading to stone formation.
- Medications: Certain medications such as antihistamines, diuretics, or antipsychotics can decrease saliva production or alter saliva composition, increasing the risk of stone formation.
- Salivary Gland Disorders: Conditions affecting the salivary glands, such as Sjögren’s syndrome or chronic inflammation (sialadenitis), can increase the risk of salivary gland duct stones.
- Anatomic Factors: Anatomic abnormalities or narrowing of the salivary ducts can predispose individuals to the formation of duct stones.
Symptoms of Salivary Gland Duct Stones
Common symptoms of salivary gland duct stones may include:
- Pain: Pain or discomfort in the affected salivary gland, particularly during eating or when the gland is stimulated to produce saliva.
- Swelling: Swelling or enlargement of the affected salivary gland, often accompanied by tenderness or redness.
- Dry Mouth: Decreased saliva production and dryness in the mouth, particularly with obstruction of the salivary ducts.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) or speaking, particularly with larger or more severe stones.
- Infection: In some cases, salivary gland duct stones may lead to inflammation or infection (sialadenitis), characterized by fever, chills, and pus discharge from the duct opening.
Treatment of Salivary Gland Duct Stones
Treatment for salivary gland duct stones depends on the size, location, and severity of symptoms. Treatment options may include:
- Saliva Stimulation: Drinking plenty of fluids, sucking on sour candies, or using sugar-free gum can help stimulate saliva flow and promote stone expulsion.
- Saliva Massage: Massaging the affected salivary gland and applying warm compresses to the area can help alleviate pain and promote stone movement.
- Sialogogues: Medications such as lemon juice or pilocarpine may be prescribed to stimulate saliva production and promote stone expulsion.
- Surgical Intervention: In cases of large or persistent stones, surgical procedures such as sialendoscopy, lithotripsy, or gland excision (sialadenectomy) may be necessary to remove the stone and alleviate symptoms.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of salivary gland duct stones, as early diagnosis and treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications such as infection or abscess formation. With proper management, individuals with salivary gland duct stones can achieve relief from symptoms and improve oral health.
18+
years
of experience

Dr. Mukesh Kumar Ramani
Dr. Mukesh Kumar Ramani is a dedicated Specialist ENT Surgeon at Aster Clinic (Aster Jubilee Medical Complex) in Burdubai, Dubai. With over 18 years of experience in the field, Dr. Ramani has garnered expertise in various aspects of Otorhinolaryngology.
He completed his MBBS from Thanjavur Medical College, Tamilnadu, India, followed by MS (ENT) from B. J. Medical College, Ahmedabad, India, and DNB from the National Board of Examinations, New Delhi, India. Dr. Ramani’s extensive academic background is complemented by his passion for delivering high-quality patient care.
