Services
We Provide
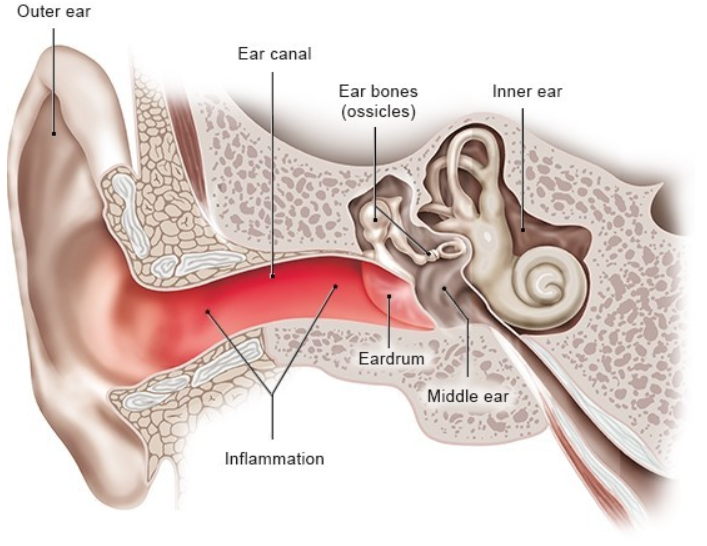
Understanding External Ear Infection
An external ear infection, also known as otitis externa or swimmer’s ear, is a common condition that affects the outer ear canal. This type of infection occurs when bacteria or fungi invade the skin lining the ear canal, leading to inflammation and discomfort. External ear infections can be painful and may interfere with hearing if left untreated. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for this condition is essential for effective management.
Diagnosis of External Ear Infection
A healthcare provider can diagnose an external ear infection through a physical examination of the ear canal using an otoscope. During the examination, they will look for signs of inflammation, redness, swelling, or discharge. In some cases, a sample of the ear discharge may be collected and sent to a laboratory for further analysis to identify the specific type of bacteria or fungi causing the infection.
Causes of External Ear Infection
External ear infections can be caused by various factors, including:
- Excess Moisture: Prolonged exposure to water, such as swimming or showering, can create a moist environment in the ear canal, making it more susceptible to infection.
- Skin Irritation: Scratching the ear canal with objects like cotton swabs or hairpins can damage the delicate skin lining, allowing bacteria or fungi to enter and cause infection.
- Foreign Objects: Inserting objects into the ear canal, such as hearing aids or earbuds, can scratch the skin and introduce bacteria, increasing the risk of infection.
- Skin Conditions: Certain skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, can make the skin of the ear canal more vulnerable to infection.
Symptoms of External Ear Infection
Common symptoms of an external ear infection may include:
- Ear Pain: Pain or discomfort in the affected ear, which may worsen when pulling on the earlobe or pressing on the tragus (the small, pointed projection in front of the ear).
- Itching: Itchiness in the ear canal.
- Redness and Swelling: Inflammation and swelling of the ear canal.
- Discharge: Drainage of fluid or pus from the ear canal.
- Decreased Hearing: Partial or complete hearing loss due to the blockage or inflammation of the ear canal.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of an external ear infection to receive appropriate treatment and prevent complications.
18+
years
of experience

Dr. Mukesh Kumar Ramani
Dr. Mukesh Kumar Ramani is a dedicated Specialist ENT Surgeon at Aster Clinic (Aster Jubilee Medical Complex) in Burdubai, Dubai. With over 18 years of experience in the field, Dr. Ramani has garnered expertise in various aspects of Otorhinolaryngology.
He completed his MBBS from Thanjavur Medical College, Tamilnadu, India, followed by MS (ENT) from B. J. Medical College, Ahmedabad, India, and DNB from the National Board of Examinations, New Delhi, India. Dr. Ramani’s extensive academic background is complemented by his passion for delivering high-quality patient care.
