Services
We Provide
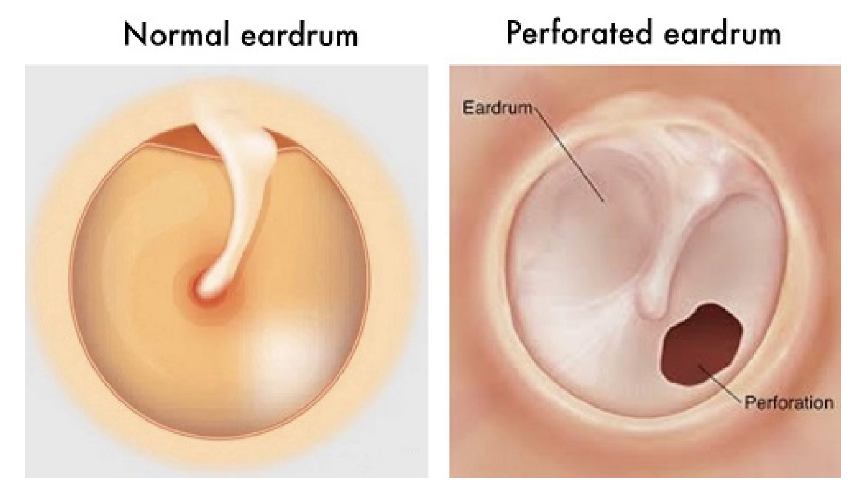
Understanding Ear Drum Perforation
Ear drum perforation, also known as a ruptured or perforated tympanic membrane, refers to a tear or hole in the thin membrane that separates the outer and middle ear. This condition can result in discomfort, hearing loss, and susceptibility to infections. Ear drum perforations can occur due to various factors, and understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is essential for managing this condition effectively.
Diagnosis of Ear Drum Perforation
An ENT Specialist can diagnose an ear drum perforation through a physical examination of the ear using an otoscope. During the examination, they will look for signs of a tear or hole in the tympanic membrane. In some cases, additional tests, such as tympanometry or audiometry, may be conducted to assess middle ear function and severity of the perforation.
Causes of Ear Drum Perforation
Ear drum perforations can occur as a result of:
- Trauma: Direct trauma to the ear, such as a blow to the head, insertion of objects into the ear canal, or sudden changes in air pressure (such as during scuba diving or air travel), can cause the ear drum to rupture.
- Infections: Severe or recurrent middle ear infections (otitis media) can lead to the accumulation of fluid and pressure behind the eardrum, eventually causing it to perforate.
- Barotrauma: Sudden changes in air pressure, such as during airplane travel or diving, can create pressure imbalances that may lead to ear drum perforation.
- Foreign Objects: Inserting objects into the ear canal, such as cotton swabs or hairpins, can damage the delicate ear drum and cause perforation.
Symptoms of Ear Drum Perforation
Common symptoms of an ear drum perforation may include:
- Ear Pain: Pain or discomfort in the affected ear, which may vary in intensity.
- Hearing Loss: Partial or temporary hearing loss, depending on the size and location of the perforation.
- Ear Drainage: Fluid or blood draining from the ear.
- Tinnitus: Ringing or buzzing sensation in the ear.
- Vertigo: Dizziness or a sensation of spinning.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you suspect an ear drum perforation, as untreated perforations can lead to complications such as infections or permanent hearing loss. Treatment for ear drum perforations may involve observation, antibiotic ear drops to prevent infections, or surgical repair (tympanoplasty) for larger perforations.
18+
years
of experience

Dr. Mukesh Kumar Ramani
Dr. Mukesh Kumar Ramani is a dedicated Specialist ENT Surgeon at Aster Clinic (Aster Jubilee Medical Complex) in Burdubai, Dubai. With over 18 years of experience in the field, Dr. Ramani has garnered expertise in various aspects of Otorhinolaryngology.
He completed his MBBS from Thanjavur Medical College, Tamilnadu, India, followed by MS (ENT) from B. J. Medical College, Ahmedabad, India, and DNB from the National Board of Examinations, New Delhi, India. Dr. Ramani’s extensive academic background is complemented by his passion for delivering high-quality patient care.
