Services
We Provide
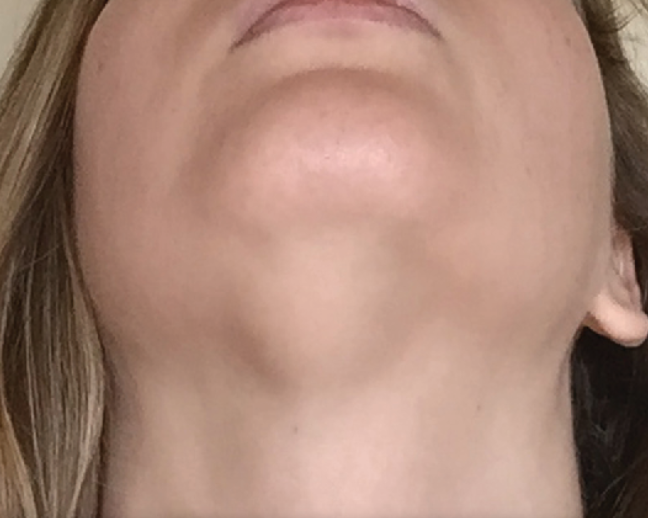
Understanding Ranula
Ranula is a type of cyst that forms in the floor of the mouth due to a blockage or rupture of the salivary glands. This condition typically appears as a painless, fluid-filled swelling or lump, often resembling a frog’s belly, hence the name “ranula,” which is derived from the Latin word for frog. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for ranula is crucial for effectively managing this condition and preventing complications.
Diagnosis of Ranula
Diagnosing ranula typically involves a comprehensive evaluation by a healthcare provider, often an oral and maxillofacial surgeon or an otolaryngologist (ear, nose, and throat specialist). During the examination, the provider may review the individual’s medical history and perform tests such as:
- Physical Examination: A physical examination of the mouth and neck to assess for signs of swelling, tenderness, or fluid-filled masses.
- Imaging Studies: Imaging studies such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scans, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be recommended to visualize the size, location, and extent of the ranula.
- Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA): Fine needle aspiration may be performed to extract fluid from the ranula for further analysis and confirmation of diagnosis.
Causes of Ranula
Ranula is caused by blockage or rupture of the salivary glands, which leads to the accumulation of saliva in the tissues of the mouth. This blockage can occur due to various factors, including:
- Obstruction: Blockage of the salivary ducts or glands due to thickened saliva, inflammation, or injury can lead to the formation of a ranula.
- Salivary Gland Disorders: Certain conditions affecting the salivary glands, such as Sjögren’s syndrome or salivary gland stones, can increase the risk of ranula formation.
- Trauma: Trauma to the mouth or face, such as a blow or injury, can damage the salivary glands and contribute to the development of ranula.
- Congenital Factors: Ranula may also occur in infants or children due to congenital abnormalities or developmental issues affecting the salivary glands.
Symptoms of Ranula
Common symptoms of ranula may include:
- Swelling: Painless swelling or lump in the floor of the mouth, often resembling a frog’s belly.
- Difficulty Swallowing or Speaking: Large ranulas may cause difficulty swallowing, speaking, or moving the tongue.
- Discomfort: Discomfort or pressure in the mouth, particularly with larger or more severe ranulas.
- Rupture: In some cases, ranulas may rupture spontaneously, leading to sudden release of fluid into the mouth and temporary relief of symptoms.
Treatment for ranula depends on the size, location, and severity of symptoms. Treatment options may include:
- Observation: Small, asymptomatic ranulas may not require treatment and can be monitored over time.
- Aspiration: Draining the fluid from the ranula using a needle (aspiration) may provide temporary relief of symptoms.
- Marsupialization: Surgical procedure to create a small opening in the ranula to allow drainage and prevent recurrence.
- Excision: Surgical removal of the ranula and affected salivary gland tissue may be necessary for larger or recurrent ranulas.
It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience symptoms of ranula, as early diagnosis and treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications such as infection or recurrence.
18+
years
of experience

Dr. Mukesh Kumar Ramani
Dr. Mukesh Kumar Ramani is a dedicated Specialist ENT Surgeon at Aster Clinic (Aster Jubilee Medical Complex) in Burdubai, Dubai. With over 18 years of experience in the field, Dr. Ramani has garnered expertise in various aspects of Otorhinolaryngology.
He completed his MBBS from Thanjavur Medical College, Tamilnadu, India, followed by MS (ENT) from B. J. Medical College, Ahmedabad, India, and DNB from the National Board of Examinations, New Delhi, India. Dr. Ramani’s extensive academic background is complemented by his passion for delivering high-quality patient care.
